Background
Unity Health Toronto is a member of Partners in Project Green (PPG) and one of Canada’s largest Catholic healthcare networks. In 2023, Unity Health Providence Healthcare participated in the Corporate Flood and Heat Risk Management program, a complimentary site assessment program, delivered by Partners in Project Green in partnership with Sustainable Technologies Evaluation Program (STEP) at Toronto and Region Conservation Authority, assessing flood and heat risks while highlighting mitigation opportunities, particularly through Low Impact Development (LID) solutions.


Aspects of the property that were evaluated included:
- Where and how stormwater drains from the property
- Condition of stormwater assets (e.g., catch basins)
- Amount of pervious vs. impervious cover
- Amount of outdoor shade cover
- Snow and ice management
- Opportunities for Low Impact Development and Green Infrastructure
With existing plans to increase tree cover by Unity Health, PPG took their assessment a step further and brought in experts from Toronto and Region Conservation Authority’s Watershed Planning and Ecosystem Science team to conduct an analysis and provide recommendations of different LID solutions to meet water quality and quantity.
Modelling Using the LID-TTT
To support the early planning stages and conceptual design for integrating stormwater management LID solutions, a desktop analysis was conducted using the Low Impact Development Treatment Train Tool (LID TTT) developed by STEP. Available Stormwater Management Plans and high-resolution Digital Elevation Model (DEM) (1 m horizontal, 0.001 m vertical resolution) were used to infer the stormwater drainage patterns across the site. The LID TTT was used to model two scenarios, pre-development and post-retrofit for three catchments along the Southeast corner of the site.
The pre-development scenario represents the site as if no development had occurred while the post-retrofit scenario represents the current state of the site with the proposed retrofits of LIDs. It analyzed overland flow paths and runoff volumes, while identifying suitable LID types and optimal placement to improve stormwater management on site.
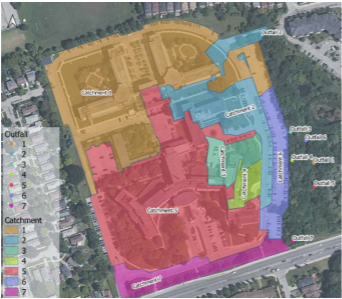
Evaluation Criteria: The results of the LID TTT evaluated all existing and proposed stormwater management criteria including erosion control, water quantity (peak flow reduction), water balance, and water quality for Total Suspended Solids (TSS) and Total Phosphorus (TP).
Findings
The LID TTT took a cost-effective approach to site design by maximizing the use of existing pervious areas, taking advantage of the property’s current grading, and minimizing disturbance to existing impervious surfaces. Through this analysis, ten LIDs were selected and evaluated against established criteria. These solutions included rain gardens, bioretention cells, bio-swales, and infiltration chambers. Despite modeling for increased precipitation patterns to account for climate change, the proposed concept plan met or exceeded all evaluation targets.
Conclusion
To support Unity Health Toronto in the planning stages of their site design, the LID TTT created a custom report which outlined several LID projects that would help achieve the goal of increased on-site stormwater infiltration, both increasing site resiliency while reducing stormwater volumes entering nearby waterways and municipal stormwater systems. Unity Health is now informed of the different projects that would improve their on-site stormwater management practices along with estimated costing.
To inquire about participating in the Corporate Flood and Heat Risk program, please contact Chaya.Chengappa@trca.ca
